diff --git a/assets/p5-intersect.svg b/assets/p5-intersect.svg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..68a6538
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/p5-intersect.svg
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+
+
diff --git a/assets/p5-intersect.txt b/assets/p5-intersect.txt
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6ac43f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/assets/p5-intersect.txt
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+OutputFile="p5-intersect.svg"
+R=.1
+Thickness=.01
+BorderColor="#616161"
+ColorMap:r="#FF7043"
+ColorMap:b="#29B6F6"
+ColorMap:g="#212121"
+FontColor="white"
+FontFamily="Ubuntu Mono"
+Xaxis="right"
+Yaxis="Down"
+Label="A"
+---
+5
+1 -2 r
+2 -1 b
+1 -1 r
+2 -2 b
+1.5 -1.5 g
+
+4
+1 5
+2 5
+3 5
+4 5
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/lib.typ b/lib.typ
index 02df0da..f7da86d 100644
--- a/lib.typ
+++ b/lib.typ
@@ -1,13 +1,13 @@
#import "template.typ": *
-#let pagebreak_until_odd() = locate(loc => {
+#let pagebreak_until_odd() = {
pagebreak()
locate(loc => if calc.even(thispage_number(loc)) {
skip_footer.update(true)
pagebreak()
skip_footer.update(false)
})
-})
+}
#let italic(body) = text(style: "italic", body)
@@ -32,6 +32,8 @@
#let frange = {$op("range")$}
#let dimrange = {$op("dim range")$}
+#let fnull = {$op("null")$}
+#let dimnull = {$op("dim null")$}
#let theme_blue = rgb("29B6F6")
#let theme_red = rgb("FF7043")
@@ -41,4 +43,6 @@
#let math_numbering(body) = {
set math.equation(numbering: "(1)")
body
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
+
+#let inprod(a,b) = {$angle.l #a,#b angle.r$}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/main.typ b/main.typ
index b604a43..871dc6c 100644
--- a/main.typ
+++ b/main.typ
@@ -507,19 +507,103 @@ $ 2>=bf(E)(abs(X))=sum_(v in V)bf(P)(v in X)=sum_(v in V)1/(n-dd(v))>=n/(n-2m sl
红蓝各 1 个点的情况的情况是平凡的,下面均假设 $n>=2$。
-(反证法)假设不存在一种合法的配对方案。从全部配对方案中选出连接的线段长度之和最短的一种方案,根据反证假设一定存在两条线段相交,设相交的两条线段的红色端点分别为点 $A$ 和点 $B$,蓝色端点分别为点 $C$ 和点 $D$,$A$ 和 $C$ 配对,$B$ 和 $D$ 配对,$A C$ 和 $B D$ 的交点为 $E$。
+(反证法)假设不存在一种合法的配对方案。从全部配对可能的方案中选出连接的线段长度之和最短的一种方案之一,根据反证假设一定存在两条线段相交。如图,设相交的两条线段的红色端点分别为点 $A$ 和点 $B$,蓝色端点分别为点 $C$ 和点 $D$,$A$ 和 $C$ 配对,$B$ 和 $D$ 配对,$A C$ 和 $B D$ 的交点为 $E$。
-/*
+#figure(image(
+ "./assets/p5-intersect.svg",
+ width: 40%
+), caption: [交点示意图])
-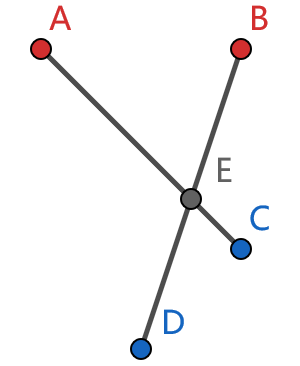
-根据三角形不等式,一定有
+根据三角形不等式(由于没有三点共线,等号一定不成立),一定有
-$$\begin{aligned}|AD|&\leq|AE|+|DE|\\|BC|&\leq|BE|+|EC|\end{aligned}$$
+#[
+#show: math_numbering
+$ abs(A D)&
+$ abs(B C)&
+]
-由于没有三点共线,等号一定不成立,这说明
+将@P5eq1 和@P5eq2 相加,得到
-$$|AD|+|BC|<|AC|+|BD|$$
+$ abs(A D)+abs(B C)
+
+根据反证假设,有 $abs(a)$、$abs(b)$、$abs(c)$、$abs(a-b)$、$abs(b-c)$ 以及 $abs(c-a)$ 均为奇整数。
+
+
+考虑定义了模 8 意义下的加法和乘法整数域 $bb(Z)_8$,容易发现其中任意一个奇数的平方一定为 1。据此,根据余弦定理和@P6eq1,得到
+
+$ 2 inprod(a,b)=abs(a)^2+abs(b)^2-abs(a-b)^2=1 $
+
+类似的,有
+
+$ 2 inprod(a,c)=1 $
+$ 2 inprod(b,c)=1 $
+]
+
+构造 $bb(Z)_8^(3 times 3)$ 上的矩阵 $B$:
+
+$ B=mat(delim: "[",
+ inprod(a,a),inprod(a,b),inprod(a,c);
+ inprod(b,a),inprod(b,b),inprod(b,c);
+ inprod(c,a),inprod(c,b),inprod(c,c)) $
+
+
+根据@P6eq1、@P6odd1、@P6odd2 与@P6odd3,有
+
+$ 2B=mat(delim: "[",
+ 2,1,1;
+ 1,2,1;
+ 1,1,2) $
+
+我们用 $dim V$ 表示线性空间 $V$ 的维数,$frange T$ 表示线性变换 $T$ 的值域,$fnull T$ 表示线性变换 $T$ 的零空间(经过 $T$ 变为 $bf(0)$ 的向量构成的子空间)。容易验证 $dimrange 2B=3$,于是
+
+#[
+#show: math_numbering
+$ dimrange B=3 $
+]
+
+另一方面,构造 $bb(Z)_8^(3 times 2)$ 上的矩阵 $A$,满足
+
+$ A=mat(delim: "[",
+ a_1,b_1,c_1;
+ a_2,b_2,c_2) $
+
+容易验证 $B=A^transpose A$,于是 $frange B subset.eq frange A^transpose$,另一方面,根据线性变换基本定理,有
+
+$ dim bb(Z)_8^2=dimrange A^transpose+dimnull A^transpose $
+
+这说明,$dimrange A^transpose<=2$,与@P6eq2 联立,得到
+
+
+$ 3=dimrange B<=dimrange A^transpose<=2 $
+
+这给出了 $3<=2$ 这样的错误的结果,故假设不成立,原命题得证。
diff --git a/scripts/diagram.svg b/scripts/diagram.svg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dc42e06
--- /dev/null
+++ b/scripts/diagram.svg
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+
diff --git a/scripts/g2s.cpp b/scripts/g2s.cpp
index 138c653..62bfed8 100644
--- a/scripts/g2s.cpp
+++ b/scripts/g2s.cpp
@@ -24,6 +24,10 @@ const float vertex_R=.1; //点的半径
const float border_width=.01; //点的边框粗细
const string border_color="#616161"; //点的边框和边的颜色
const map mp{{"b","#29B6F6"},{"r","#FF7043"}}; //颜色映射表
+const string label = "A"; // 标签格式
+const string font_family = "Ubuntu Mono"; // 字体
+const string font_color = "white"; // 标签颜色
+const float output_scale = 100;
vec calc(vec a,vec b)
{
@@ -69,15 +73,17 @@ int main(int argc,char** argv)
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i].x-=X,p[i].y-=Y;
X=(maxX-X)+(maxX-minX)*XR;
Y=(maxY-Y)+(maxY-minY)*YR;
- cout<<""<"<
+"<